Scaling Laravel with Hexagonal Architecture
Laravel’s default MVC structure works well for small projects but quickly becomes hard to maintain and scale as the application grows. Adopting Hexagonal Architecture combined with isolated domains improves modularity, reduces coupling, and makes your system more resilient to changes, saving time, money, and developer effort.
Real-World Problem
In large Laravel applications, features often become tightly coupled within controllers and models. Adding new functionality or modifying existing behavior can inadvertently break unrelated parts of the system. Teams face long development cycles, higher maintenance costs, and increased risk of bugs.
My Approach / Decision
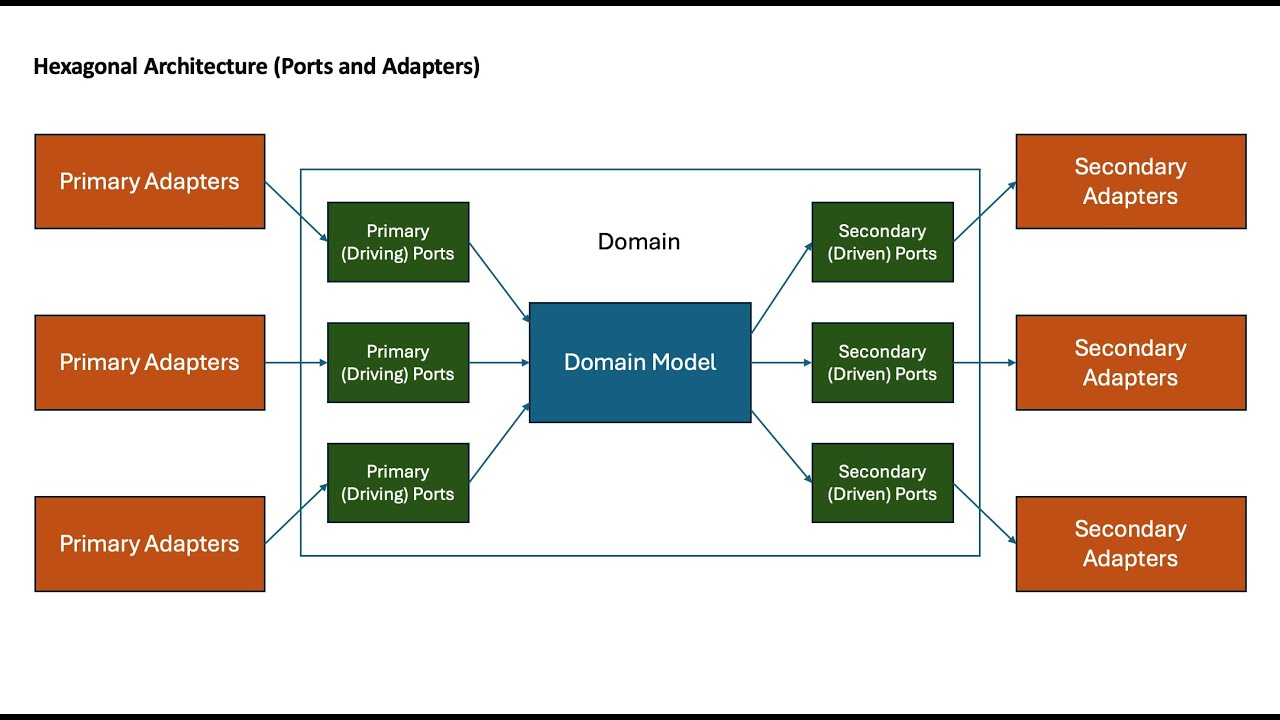
I adopted a Hexagonal Architecture approach with isolated domain layers. Each domain handles its own business logic, and adapters manage communication with external systems like databases or APIs. This separation ensures that changes in one part of the system don’t ripple across unrelated modules.
Implementation
1. Define Domain Layer: Create App/Domains/Orders for order management.
2. Port: (Interface)
namespace App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Ports;
interface OrderRepositoryPort
{
public function save(array $data): object;
}2. Adapter: Database adapter example
namespace App\Domains\Orders\Adapters;
use App\Domains\Orders\Ports\OrderRepositoryPort;
use App\Models\Order;
class OrderRepository implements OrderRepositoryPort
{
public function save(array $data): object
{
return Order::create($data);
}
}3. Service: Domain based service example
namespace App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Services;
use App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Ports\OrderRepositoryPort;
class OrderService
{
protected OrderRepositoryPort $repository;
public function __construct(OrderRepositoryPort $repository)
{
$this->repository = $repository;
}
public function createOrder(array $data)
{
// Example domain logic
$data['status'] = 'pending';
// Call the port to save the data
return $this->repository->save($data);
}
}
4. Controller: Domain based controller example
namespace App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Controllers;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Services\OrderService;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class OrderController extends Controller
{
protected OrderService $service;
public function __construct(OrderService $service)
{
$this->service = $service;
}
public function store(Request $request)
{
$this->service->createOrder($request->all());
return response()->json(['status' => 'success']);
}
}5. Service provider
namespace App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Providers;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
use App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Ports\OrderRepositoryPort;
use App\Domains\Orders\Adapters\OrderRepository;
class OrdersServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register(): void
{
// Bind port to adapter
$this->app->bind(OrderRepositoryPort::class, OrderRepository::class);
}
public function boot(): void
{
//
}
}
6. Register service provider
Then register it in config/app.php or via a DomainServiceProvider auto-loader if you have one:
App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Providers\OrdersServiceProvider::class,Explanation
OrderServicedoes not know the concrete implementation of the repository.You can swap
OrderRepositorywith another adapter (API, in-memory, etc.) without changing the service.This keeps the domain isolated, fulfilling Hexagonal principles.
Security & Risk Considerations
With isolated domains, it’s easier to apply consistent validation and authorization per module. Ensure adapters sanitize inputs and handle exceptions properly. Misconfigured dependency injection or direct access to models outside adapters can still introduce security risks.
Results / Outcome
Post-refactor, the application became modular, tests are easier to write, new features integrate faster, and developers can work in parallel on isolated domains without conflicts. Maintenance costs dropped and the codebase is now more resilient to change.
Key Takeaways
Hexagonal Architecture improves modularity and reduces coupling.
Isolated domains allow independent development and testing.
Adapters manage external interactions safely and consistently.
The approach reduces long-term maintenance costs and development time.
Security and input validation are easier to enforce per domain.
Who This Is For
Laravel developers, backend engineers, technical leads, and teams managing large-scale applications who want scalable, maintainable, and secure architectures.
Best Practice
Use a central DomainServiceProvider to auto-load domain-specific migrations, routes, and service providers. This reduces boilerplate, keeps domains isolated, and makes scaling with new domains seamless.
This approach ensures your Laravel application remains modular, maintainable, and ready for future growth or microservice integration.
<?php
namespace App\Providers;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\File;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class DomainServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register(): void
{
$this->discoverDomains(function ($domainPath, $domainName) {
// 1. Auto-register Service Providers
$providersPath = $domainPath . '/Domain/Providers';
if (File::isDirectory($providersPath)) {
$providerFiles = File::files($providersPath);
foreach ($providerFiles as $file) {
/**
* Convert file path to Class Name
* Example: App\Domains\Orders\Domain\Providers\OrderServiceProvider
*/
$className = 'App\\Domains\\' . $domainName . '\\Domain\\Providers\\' . $file->getFilenameWithoutExtension();
if (class_exists($className)) {
$this->app->register($className);
}
}
}
});
}
public function boot(): void
{
$domainsPath = base_path('app/Domains');
// 1. Check if the directory exists to avoid errors
if (!File::isDirectory($domainsPath)) {
return;
}
// 2. Get all subdirectories within app/Domains
$directories = File::directories($domainsPath);
foreach ($directories as $domainPath) {
/**
* $domainPath is the full absolute path, e.g., /var/www/app/Domains/Orders
*
* 3. Auto-load Migrations
* Path: app/Domains/{Domain}/Domain/Migrations
*/
$migrationPath = $domainPath . '/Domain/Migrations';
if (File::isDirectory($migrationPath)) {
$this->loadMigrationsFrom($migrationPath);
}
/**
* 4. Auto-load Routes
* Path: app/Domains/{Domain}/Domain/routes.php
*/
$routeFile = $domainPath . '/routes.php';
if (File::exists($routeFile)) {
Route::middleware('web')
->group($routeFile);
}
}
}
/**
* Helper to avoid repeating the directory scanning logic.
*/
protected function discoverDomains(callable $callback): void
{
$domainsPath = base_path('app/Domains');
if (!File::isDirectory($domainsPath)) {
return;
}
$directories = File::directories($domainsPath);
foreach ($directories as $path) {
$domainName = basename($path); // e.g., "Orders"
$callback($path, $domainName);
}
}
}
